THE OTHER SIDE OF THE STORY

Similarities with our Present World
Average global temperatures in the Early Carboniferous Period were hot- approximately 20° C (68° F). However, cooling during the Middle Carboniferous reduced average global temperatures to about 12° C (54° F). As shown on the chart below, this is comparable to the average global temperature on Earth today!
Similarly, atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Early Carboniferous Period were approximately 1500 ppm (parts per million), but by the Middle Carboniferous had declined to about 350 ppm -- comparable to average CO2 concentrations today!
Earth's atmosphere today contains about 380 ppm CO2 (0.038%). Compared to former geologic times, our present atmosphere, like the Late Carboniferous atmosphere, is CO2- impoverished! In the last 600 million years of Earth's history only the Carboniferous Period and our present age, the Quaternary Period, have witnessed CO2 levels less than 400 ppm.
Global Temperature and Atmospheric CO2 over Geologic Time
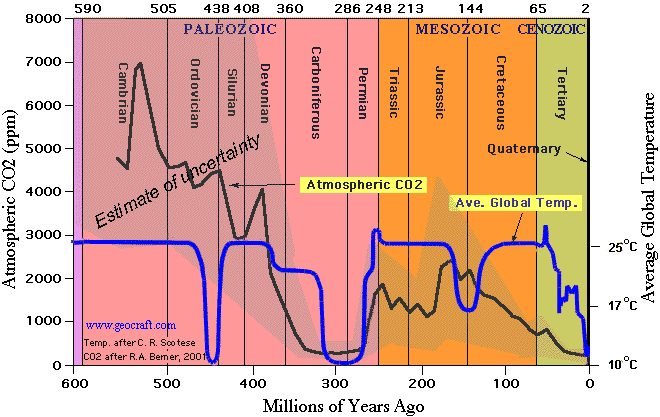
Late Carboniferous to Early Permian time (315 mya -- 270 mya) is the only time period in the last 600 million years when both atmospheric CO2 and temperatures were as low as they are today (Quaternary Period ).
There has historically been much more CO2 in our atmosphere than exists today. For example, during the Jurassic Period (200 mya), average CO2 concentrations were about 1800 ppm or about 4.7 times higher than today. The highest concentrations of CO2 during all of the Paleozoic Era occurred during the Cambrian Period, nearly 7000 ppm -- about 18 times higher than today.
The Carboniferous Period and the Ordovician Period were the only geological periods during the Paleozoic Era when global temperatures were as low as they are today. To the consternation of global warming proponents, the Late Ordovician Period was also an Ice Age while at the same time CO2 concentrations then were nearly 12 times higher than today-- 4400 ppm. According to greenhouse theory, Earth should have been exceedingly hot. Instead, global temperatures were no warmer than today. Clearly, other factors besides atmospheric carbon influence earth temperatures and global warming.
from Climate and the Carboniferous Period
No comments:
Post a Comment